Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
br Experimental br Acknowledgment This work was supported in
2022-04-06
Experimental Acknowledgment This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. Glyoxalase I (GLO1) is a zinc enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of a hemithioacetal, formed from glut
-
br Conclusion br Acknowledgments br Introduction Throughout
2022-04-06
Conclusion Acknowledgments Introduction Throughout history, there is literature that supports the notion that animals can be perceived as “healing”. Overall, there is an increased interest in the general field of Animal Assisted Therapy (AAT). Though the field of equine-facilitated psychoth
-
Tight junctions regulate the transfer
2022-04-06
Tight junctions regulate the transfer of ions as well as small molecules across endothelial barriers (Li et al., 2015). We also investigated whether resistin affects tight junctions, which play an important role in the conformation of polarized endothelial barriers (Matsuzaki et al., 2010). A previo
-
Unlike our present results in week old months females
2022-04-06
Unlike our present results in 4–12-week-old (~1–3 months) females, where a high-fat-diet-induced increase in body weight was evident, Schmidt et al. exposed male glut3 mice to a similar high-fat diet (60% kilocalories from fat) and observed no change in body weight, plasma glucose or insulin concent
-
br Conflict of interest br Acknowledgements br
2022-04-06
Conflict of interest Acknowledgements Introduction Second generation antipsychotic drugs (SGAs) such as olanzapine are widely used in treating individuals with schizophrenia and bi-polar disorder and are increasingly prescribed for other conditions such as anxiety (Pringsheim and Gardner, 2
-
erk inhibitor Interruption of glucagon signaling pathway tar
2022-04-06
Interruption of glucagon signaling pathway targeting glucagon receptor (GCGR) by gene knockout, antisense oligonucleotides or specific antagonists induces α-cell hyperplasia and alleviates hyperglycemia and other metabolic symptoms in diabetic animals and patients [[7], [8], [9]]. Here we used a ful
-
In the second part of this study
2022-04-06
In the second part of this study, we investigated the influence of GH on the Cy3 TSA Fluorescence System Kit of the ghrelin receptor, GHSR-1a, at the mRNA and peptide levels in cultured whole follicles. Regulation of the expression of GHSR-1a has a key role in the actions of ghrelin in target tissue
-
As many of the above studies highlight several
2022-04-06
As many of the above studies highlight, several decades of research on Cx43 has revealed that many of these functional roles are attributed to the C-terminal domain (CT) of this protein which cannot be explained by the formation and existence of intercellular channels. Recent findings on the existen
-
D appears to be important for receptor function as
2022-04-06
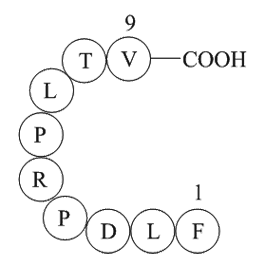
D83 appears to be important for receptor function as a mutation to an alanine produced a non-functional channel. Interestingly, maintaining the charge as in D83E produced only a small reduction in GABA sensitivity. Other mutations at this position which included residues capable of hydrogen bonding
-
In summary we have discovered
2022-04-02
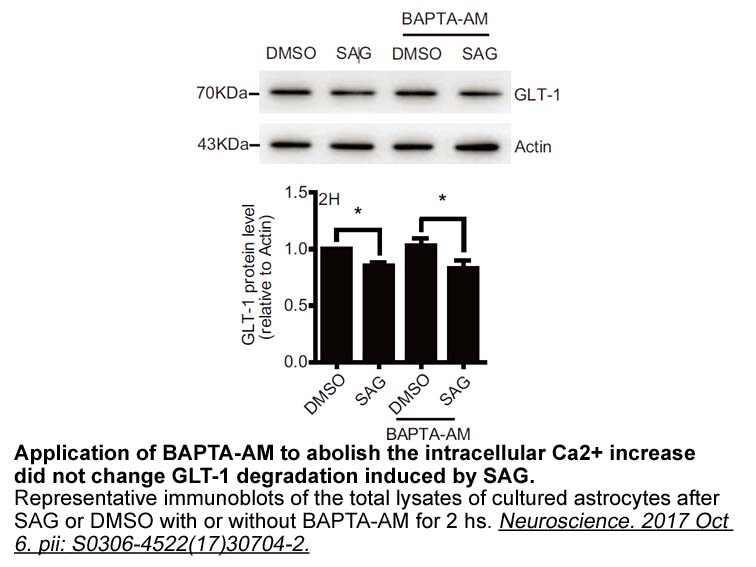
In summary, we have discovered the first examples of movement of Asp189 upon binding to fXa inhibitors. A series of novel and potent fXa inhibitors with a phenyltriazolinone P moiety were identified. Although the general binding mode compared to our previously-reported fXa inhibitors was maintained,
-
br Acknowledgments R Dalmann has obtained a bourse Cifre
2022-04-02
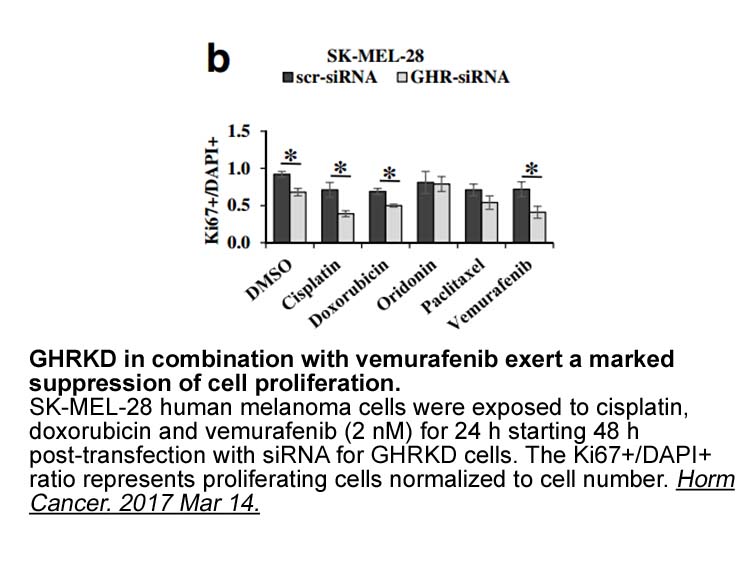
Acknowledgments R. Dalmann has obtained a “bourse Cifre” (grant 304/2011) from the ‘Association Nationale de la Recherche Technique’ and Bristol-Myers-Squibb. Introduction Endocannabinoids, their molecular targets (receptors), their synthetic and degrading enzymes and proteins that transport
-
Together the epigenetic interplay revealed in this study ena
2022-04-02
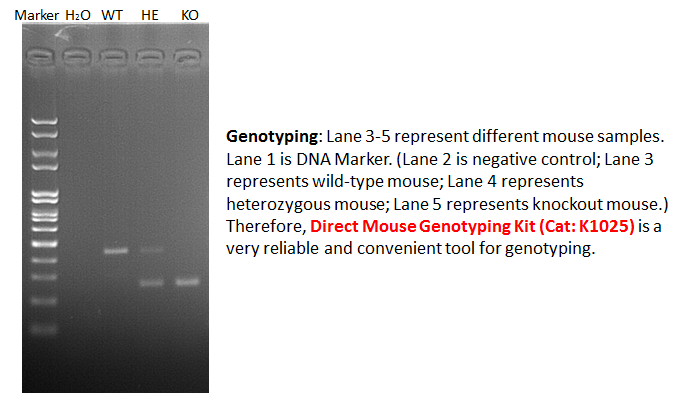
Together, the epigenetic interplay revealed in this study enabled us to expand the therapeutic potential of EZH2is from hematological malignances to solid tumors. In solid tumors, EZH2i-driven transcriptional changes are shown to be dispensable of H3K27me-regulated transcriptional network. Instead,
-
The current study aimed to understand the roles and the
2022-04-02
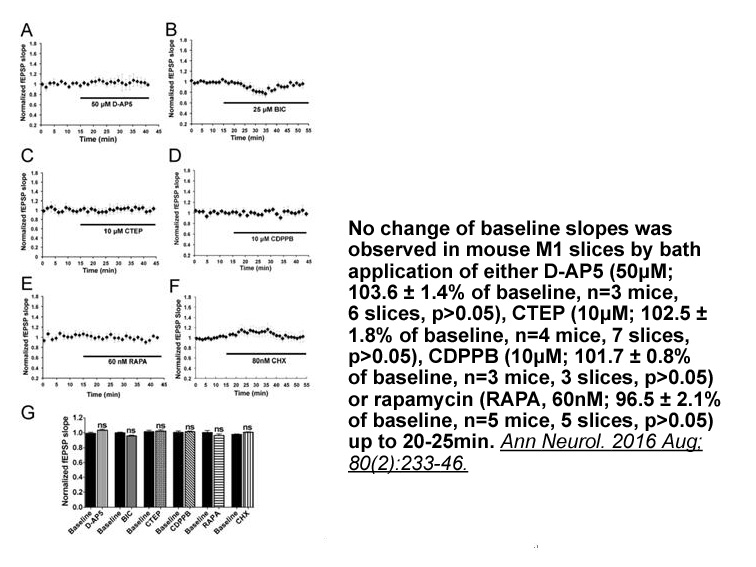
The current study aimed to understand the roles and the underlying mechanisms of XIST in LSCC, by focusing on the regulation by miR-124-3p, which was previously identified as a target of XIST [12]. We found that the XIST expression is positively correlated with the stages of LSCC in patients. Knockd
-
br Materials and methods br
2022-04-02

Materials and methods Results Discussion The roles of EZH2 during oocyte maturation, early embryogenesis, and somatic cell nucleus transfer (SCNT) have been studied extensively in mouse [12,30]. How it functions during porcine preimplantation development, especially the maternal effect, how
-
The organ culture method has previously shown
2022-04-02
The organ culture method has previously shown to be a suitable model for investigations of receptor upregulation on vascular smooth muscle cells (Adner et al., 1996). In our study, the organ culture method was applied in order to examine whether LPS from P.g. was capable of altering the gene express
15384 records 495/1026 page Previous Next First page 上5页 491492493494495 下5页 Last page