Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2018-07
-
br Conclusions Several lines of evidence
2025-03-01
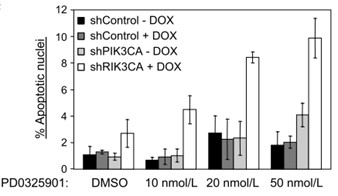
Conclusions Several lines of evidence have been established, which support the adenosine kinase hypothesis of epileptogenesis, which is based on a sequence of events leading from acute TTNPB injury to initial downregulation of ADK, rise in extracellular adenosine, changes in astrocytic adenosine
-
CI 976 Similarly Dilma et al tried to
2025-03-01
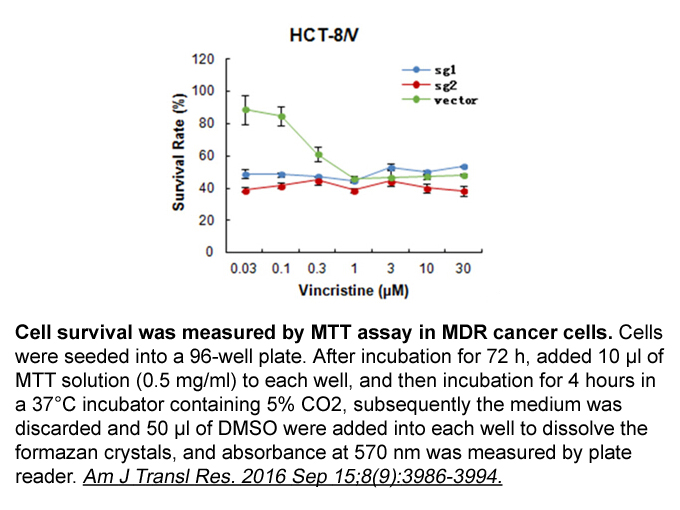
Similarly Dilmaç et al. [16] tried to assess the diagnostic value of adenosine deaminase activity in sputum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, their aim was to determine and compare sputum ADA activity in pulmonary tuberculosis, lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) pati
-
br Results br Discussion The present study uncovers a role
2025-03-01
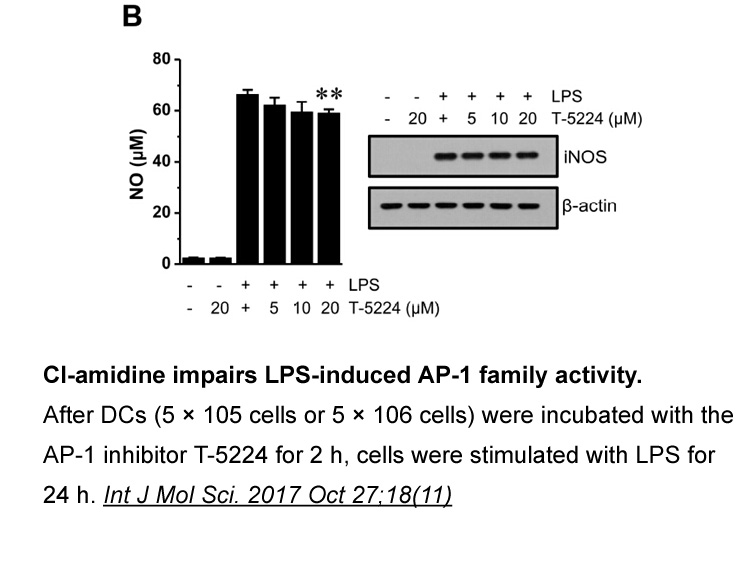
Results Discussion The present study uncovers a role of calpain, a family of calcium-dependent protease, in regulating postsynaptic differentiation at the NMJ. Cholinergic activation stimulates calpain, whose inhibition stabilizes AChR clusters in cultured muscle Exemestane and in agrin mutan
-
It is important to note that
2025-02-28

It is important to note that stable amnesia is, apparently, a general biological phenomenon and can be found in different animal species. In studies on rats, it was found that if reconsolidation of conditioned olfactory aversion memory was impaired by the antagonist of NMDA glutamate receptors, amne
-
Introduction Cancer which is responsible for a
2025-02-28
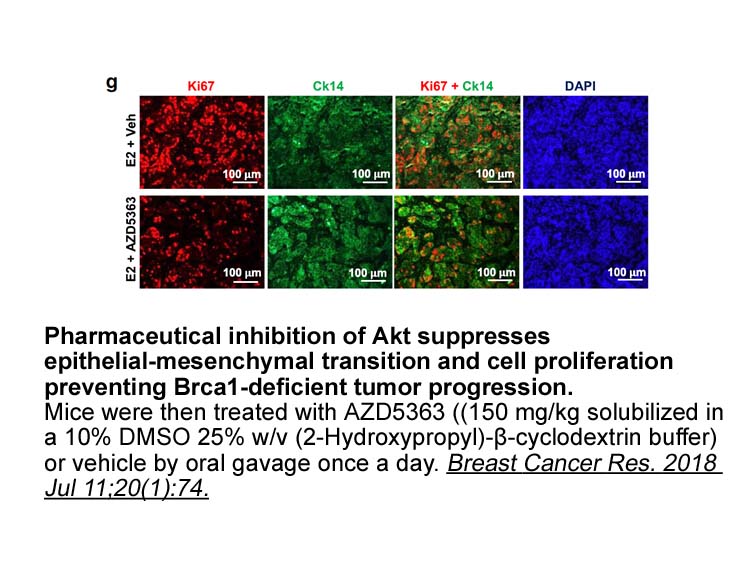
Introduction Cancer, which is responsible for a million deaths each year, is universally feared, and approximately 50% of newly diagnosed cases can be cured [1]. The existing cancer treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or a combination of them, are quickly losing efficacy. The
-
We found a protective effect of the GTCC haplotype
2025-02-28
We found a protective effect of the GTCC haplotype against ED, which is reflected by its association with increased IIEF in patients with clinical ED. Further studies are required to determine the functional implications of these genetic markers combined in specific haplotypes blocks. Indeed, we fou
-
Human hepatocyte transplantation resulted in
2025-02-28
Human hepatocyte transplantation resulted in some animals with relatively sparse repopulation while others had >90% of their liver containing human hepatocytes. The presence of circulating human albumin varied based on the amount of repopulation as the degree of humanization is reported to correlate
-
The mechanism governing how mechanotransduction signals regu
2025-02-28
The mechanism governing how mechanotransduction signals regulate a number of genes involved in cartilage hemostasis remains unclarified. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are activated by static and dynamic compression of cartilage (31 32). c-Fos/AP-1 is downstream of the MAPK pathway
-
Although the interactions of PhLP with G and its other
2025-02-28
Although the interactions of PhLP with Gβγ and its other partners have been convincingly documented through in vitro studies, it is not clear how PhLP controls GDC-0449 signaling in vivo. C. elegans provides a powerful genetic model to analyze Phosducin function and study its interacting partners i
-
br Results br Discussion Evaluation of antimicrobial usage i
2025-02-28
Results Discussion Evaluation of antimicrobial usage is standardized using the DDD as a recommended strategy for comparison with similar hospitals [13]. The use of risk adjustment is needed to overcome the challenge of benchmarking. Two patient characteristics are associated with clinical outc
-
Of the infants in the study there
2025-02-28
Of the 580 infants in the study, there were 106 twin deliveries and 10 triplet deliveries. There was no difference in prenatal antibiotic exposure between multiple and singleton births. Nevertheless, analysis of maternal antibiotic use was based on the 309 individual mothers who were provided Almore
-
Due to anatomical and physiologic characteristics of the eye
2025-02-28

Due to anatomical and physiologic characteristics of the eye, administration of ophthalmic medicines is difficult and many studies showed that only approximately 5% of the administrated dose are absorbed by intraocular tissues, making the treatment unfeasible for diseases located in posterior segmen
-
br Conclusion We have identified
2025-02-28
Conclusion We have identified three non-competitive inhibitors of the human and porcine APN with Ki values in the μM range, by combining virtual screening and kinetic assays. Molecular docking simulations suggest these novel inhibitors block APN activity by an alternative mechanism to Zn coordina
-
Recently a Phase III study demonstrated that
2025-02-28
Recently, a Phase III study demonstrated that alectinib, the second-generation ALK inhibitor, might have a better response to ALK-rearrangement patients than crizotinib [10]. Should alectinib replace crizotinib as the frontline treatment for ALK-rearranged patients? Or should those patients be treat
-
br Introduction The traditional Chinese medicine
2025-02-28
Introduction The traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), Ganoderma (G.) lucidum Karst is a well-known mushroom which has been used clinically in some Asian countries. It is termed “Lingzhi” in China, “Reishi” in Japan and “Yeongji” in Korea. It has long been used in TCM for the promotion of longevity
15369 records 15/1025 page Previous Next First page 上5页 1112131415 下5页 Last page